On This Page
MLE Request + Response
Enable Message-Level Encryption
IMPORTANT
There are additional tasks you must complete before you can
enable message-level encryption. See the Prerequisites for MLE section below.
Message-Level Encryption (MLE) enables you to store information or communicate
with other parties while helping to prevent uninvolved parties from understanding the
stored information. Enabling MLE requires you to create a
REST-Certificate
for
encrypting your requests and a REST – API Response MLE
key for decrypting
received responses. If your organization is using a meta key, the portfolio account or
merchant account that created the meta key must also create the REST – API Response MLE
key.MLE provides enhanced security for message payload by using an asymmetric encryption
technique (public-key cryptography). The message encryption is implemented with
symmetric encryption using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Galois Counter Mode (GCM)
with 256-bit key size. The encryption of keys is supported using RSA Optimal Asymmetric
Encryption Padding (OAEP) with 2048-bit key size. The encryption service is based on
JSON Web Encryption (JWE), works on top of SSL and requires separate key-pairs for
request and response legs of the transaction.
MLE is required for APIs that primarily deal with sensitive transaction data,
both financial and non-financial. These are the types of sensitive transaction data:
- Personal identification information (PII)
- Personal account number (PAN)
- Personal account information (PAI)
MLE is supported when using JSON web tokens.
Each of these authentication schemes uses an encrypted payload, called the
JWE
. A
JWE token has these five components, with each component separated by a period (.): - JOSE header containing four elements:"alg": "RSA-OAEP-256", // The algorithm used to encrypt the CEK. "enc": "A256GCM", // The algorithm used to encrypt the message. "iat": "1702493653", // The current timestamp in milliseconds. "kid": "keyId" // The serial number of shared public cert for encryption of CEK.
- JWE encrypted key
- JWE initialization vector
- JWE additional authentication data (AAD)
- JWE ciphertext and authentication tag
Prerequisites for MLE
Before you can enable message-level encryption (MLE), you must complete these requirements:
- Verify that theCybersourceproducts you are integrating support MLE.
- Ensure that your system is configured to read the public key and encrypt the API payload.
Create or Submit a REST—API Response MLE Key
Before you can enable your system to support MLE, you must create or upload
a
REST—API response MLE
certificate. After creating or uploading the certificate,
you can extract the certificate's key to begin enabling MLE.Follow these steps to create or submit an API Response MLE certificate in
the
Business Center
:- Log in to theBusiness Center:
- On the left navigation panel, choosePayment Configuration > Key Management.
- Click+ Generate keyon the Key Management page.
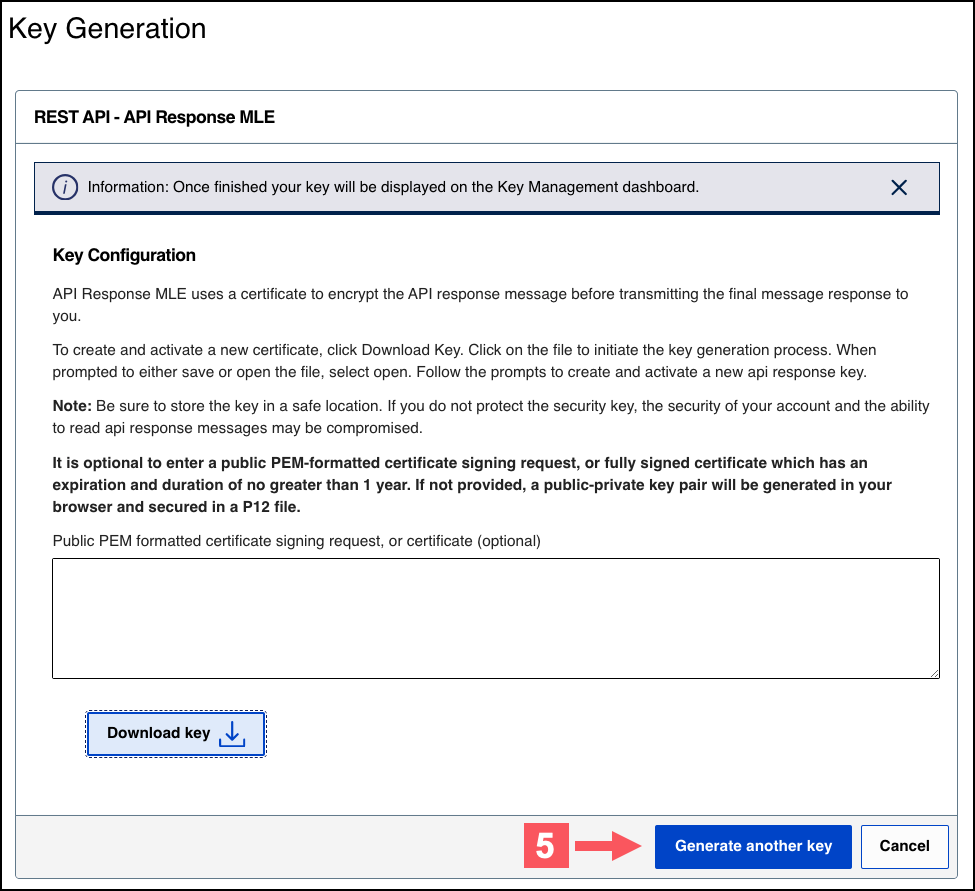
- Under REST APIs, chooseREST – API Response MLE, and then clickGenerate key.

- Choose one of these options to download your key:
- To create a new API response MLE certificate, clickDownload key
.
- To upload your own certificate, enter your public PEM-formatted certificate in the text box, and then clickDownload key
. The
.pemfile downloads to your desktop. If prompted by your system, approve the location to which the file downloads.
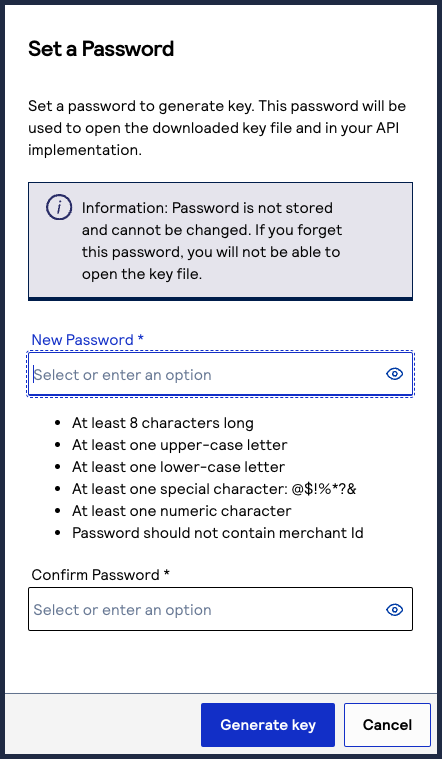
- If you are creating a certificate, the Set a Password window appears. Create a password for the certificate by entering the password into theNew PasswordandConfirm Passwordfields, and then clickGenerate key.The.p12file downloads to your desktop. If prompted by your system, approve the location to which the key downloads.
 To create or upload another key, clickGenerate another key. To view all of your created keys, go to the Key Management page.IMPORTANTSecurely store the.p12file and password in your system. These credentials are required in order to implement certain products, and you must be able to access them.
To create or upload another key, clickGenerate another key. To view all of your created keys, go to the Key Management page.IMPORTANTSecurely store the.p12file and password in your system. These credentials are required in order to implement certain products, and you must be able to access them. - ClickCancel.The Key Management page appears.
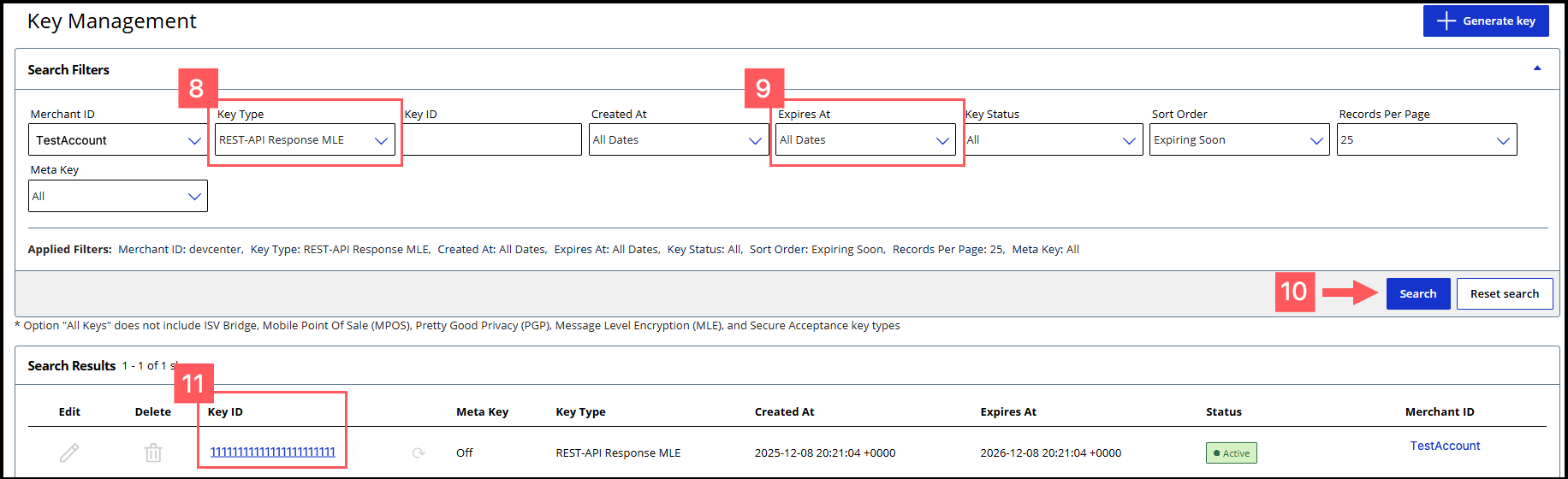
- Click theKey Typefilter and chooseREST-API Response MLE.
- Click theExpires Atfilter and chooseAll Dates.
- ClickSearch.
- Find the REST–API Response key that you created in the Search Results table and save its key ID.The key ID is needed to test and configure your system to use MLE.
- Test Your REST–API Response MLE Key
- To test your REST–API Response key, see Test Your REST—API Response MLE Key.
Overview of MLE Setup Tasks
Use the information in this section to configure your system with a custom MLE using
JWTs.
If you do not want to set up a custom MLE, you can use the REST Client SDK instead. For
more information, see the REST Client SDKs in GitHub.
Figure:
Overview of MLE Set-Up Tasks

- Import the required programming libraries for your system.
- Import these three certificates:
- Signing certificate (REST – Certificate).
- MLE request certificate (SJC public certificate)
- MLE response certificate (REST – API Response MLE)
- Encrypt the JSON request message using a JSON Web Encryption (JWE) that uses the SJC public certificate.
- Create the HTTP body in this format:{"encryptedRequest": ".JWE-with-SJC"}
- Create the JSON Web Signature (JWS) payload with these JWT payload fields and your signing certificate's private key. For descriptions of these fields, see the Headers table and Message Body Fields table in Construct Messages Using JSON Web Tokens.
- Header Fields
- alg
- kid
- type
- Message Body Fields
- digestAlgorithm
- digestof the HTTP body
- exp
- iat
- iss
- jti
- request-host
- request-method
- request-resource-path
- v-c-jwt-version
- v-c-merchant-id
- v-c-response-mle-kidfrom the MLE response certificate.
- Sign the JWS with your signing certificate and send it asAuthorization: Bearer, such as a P12 certificate.
- Receive an encrypted response and decrypt it with the MLE private key. You will receive the response in this format:{"encryptedResponse": "JWE-with-ResponseMLECertificate"}The JWE contains a JOSE header containing these four default elements:"alg": "RSA-OAEP-256", // The algorithm used to encrypt the CEK. "enc": "A256GCM", // The algorithm used to encrypt the message. "iat": "1702493653", // The current timestamp in milliseconds. "kid": "keyId" // The serial number of thev-c-api-response-mle-kidfrom the authentication JWS in step 5.
Java Example: Enabling MLE Using JWTs
This example describes a possible way in which to configure your system to create a
custom MLE with JWTs. These steps use the Java programming language.
- Import your preferred libraries to support MLE. In this step, the configuration uses Java leveraging the open source Nimbus JOSE and Bouncy Castle libraries.// Nimbus JOSE + JWT import com.nimbusds.jose.JWEAlgorithm; import com.nimbusds.jose.JWEHeader; import com.nimbusds.jose.JWEObject; import com.nimbusds.jose.JWSAlgorithm; import com.nimbusds.jose.JWSHeader; import com.nimbusds.jose.JWSObject; import com.nimbusds.jose.JOSEObjectType; import com.nimbusds.jose.EncryptionMethod; import com.nimbusds.jose.Payload; import com.nimbusds.jose.crypto.RSADecrypter; import com.nimbusds.jose.crypto.RSAEncrypter; import com.nimbusds.jose.crypto.RSASSASigner; // BouncyCastle (PEM parsing + cert conversion) import org.bouncycastle.cert.X509CertificateHolder; import org.bouncycastle.cert.jcajce.JcaX509CertificateConverter; import org.bouncycastle.openssl.PEMKeyPair; import org.bouncycastle.openssl.PEMParser; import org.bouncycastle.openssl.jcajce.JcaPEMKeyConverter;
- Import the signing, MLE, and SJC certificates. The P12 certificate as the signing certificate.public final class KeyPairMaterial { public final PrivateKey privateKey; public final X509Certificate cert; public KeyPairMaterial(PrivateKey k, X509Certificate c) { this.privateKey = k; this.cert = c; } } public final class CryptoMaterialDual { // Merchant: JWS (REST – Certificate) public final KeyPairMaterial signingCert; // Merchant: Response decryption (API Response MLE) public final KeyPairMaterial responseCert; // Platform encryption cert (SJC) public final X509Certificate sjcCert; public CryptoMaterialDual(KeyPairMaterial signingCert, KeyPairMaterial responseCert, X509Certificate sjcCert) { this.signingCert = signingCert; this.responseCert = responseCert; this.sjcCert = sjcCert; } }
- Unpack your imported certificates into a usable format for your system.Create this method for your system to read your.p12file, if you are using the P12 certificate.static KeyPairMaterial loadKeyPairFromP12(Path p12Path, char[] password, String keyAlias) throws Exception { KeyStore ks = KeyStore.getInstance("PKCS12"); try (InputStream in = Files.newInputStream(p12Path)) { ks.load( in , password); } KeyStore.PrivateKeyEntry entry = (KeyStore.PrivateKeyEntry) ks.getEntry( keyAlias, new KeyStore.PasswordProtection(password)); return new KeyPairMaterial(entry.getPrivateKey(), (X509Certificate) entry.getCertificate()); }Create this method for your system to read the PEM chain and private key.static KeyPairMaterial loadKeyPairFromPem(Path certificateChainPem, String privateKeyPem) throws Exception { X509Certificate leaf = readPemCerts(certificateChainPem).get(0); PrivateKey key = readPkcs8PrivateKey(privateKeyPem); return new KeyPairMaterial(key, leaf); }Create this method for your system to read the SJC from the.p12file or PEM chain.static X509Certificate loadSjcFromP12(Path p12Path, char[] password, String sjcAlias) throws Exception { KeyStore ks = KeyStore.getInstance("PKCS12"); try (InputStream in = Files.newInputStream(p12Path)) { ks.load( in , password); } return (X509Certificate) ks.getCertificate(sjcAlias); } static X509Certificate loadSjcFromPem(Path sjcCertPem) throws Exception { return readPemCerts(sjcCertPem).get(0); }Create this method to include PEM helper functions.static List < X509Certificate > readPemCerts(Path pemPath) throws Exception { try (Reader r = Files.newBufferedReader(pemPath); org.bouncycastle.openssl.PEMParser p = new org.bouncycastle.openssl.PEMParser(r)) { var xconv = new org.bouncycastle.cert.jcajce.JcaX509CertificateConverter().setProvider("BC"); List < X509Certificate > certs = new ArrayList < > (); Object o; while ((o = p.readObject()) != null) { if (o instanceof org.bouncycastle.cert.X509CertificateHolder h) certs.add(xconv.getCertificate(h)); } return certs; } } static PrivateKey readPkcs8PrivateKey(String pem) throws Exception { try (var parser = new org.bouncycastle.openssl.PEMParser(new StringReader(pem))) { Object o = parser.readObject(); var conv = new org.bouncycastle.openssl.jcajce.JcaPEMKeyConverter().setProvider("BC"); if (o instanceof org.bouncycastle.asn1.pkcs.PrivateKeyInfo pki) return conv.getPrivateKey(pki); if (o instanceof org.bouncycastle.openssl.PEMKeyPair kp) return conv.getPrivateKey(kp.getPrivateKeyInfo()); throw new IllegalArgumentException("Expect PKCS#8 private key PEM"); } }
- Create these methods as helpers for encrypting and signing.static String kidFromCert(X509Certificate cert) { String dn = cert.getSubjectDN().getName().toUpperCase(); int i = dn.indexOf("SERIALNUMBER="); if (i >= 0) { int j = dn.indexOf(",", i); if (j < 0) j = dn.length(); return dn.substring(i + "SERIALNUMBER=".length(), j).trim(); } return cert.getSerialNumber().toString(); } static String encryptToJwe(String json, X509Certificate sjcCert) throws Exception { var header = new com.nimbusds.jose.JWEHeader.Builder( com.nimbusds.jose.JWEAlgorithm.RSA_OAEP, com.nimbusds.jose.EncryptionMethod.A256GCM) .contentType("JWT") .keyID(kidFromCert(sjcCert)) .build(); var jwe = new com.nimbusds.jose.JWEObject(header, new com.nimbusds.jose.Payload(json)); jwe.encrypt(new com.nimbusds.jose.crypto.RSAEncrypter((RSAPublicKey) sjcCert.getPublicKey())); return jwe.serialize(); } static String sha256Base64(String body) throws Exception { MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256"); return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(md.digest(body.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))); } static String signAsJws(String payload, KeyPairMaterial signingCert) throws Exception { var header = new com.nimbusds.jose.JWSHeader.Builder(com.nimbusds.jose.JWSAlgorithm.RS256) .keyID(kidFromCert(signingCert.cert)) .type(com.nimbusds.jose.JOSEObjectType.JWT) // typ=JWT .build(); var jws = new com.nimbusds.jose.JWSObject(header, new com.nimbusds.jose.Payload(payload)); jws.sign(new com.nimbusds.jose.crypto.RSASSASigner(signingCert.privateKey)); return jws.serialize(); } static String decryptJwe(String compactJwe, KeyPairMaterial responseCert) throws Exception { var jwe = com.nimbusds.jose.JWEObject.parse(compactJwe); jwe.decrypt(new com.nimbusds.jose.crypto.RSADecrypter((RSAPrivateKey) responseCert.privateKey)); return jwe.getPayload().toString(); }
- Create a class that uses the methods described in the above steps to encrypt and decrypt your payloads with MLE using JWTs.// Example mix: // - REST – Certificate from PKCS#12 // - API Response MLE from PEM // - SJC from PEM KeyPairMaterial signingCert = loadKeyPairFromP12( Paths.get("merchant.p12"), "password".toCharArray(), "merchant"); KeyPairMaterial responseCert = loadKeyPairFromPem( Paths.get("api_response_mle_chain.pem"), Files.readString(Paths.get("api_response_mle_private_key.pem"))); X509Certificate sjc = loadSjcFromPem(Paths.get("sjc_certificate.pem")); CryptoMaterialDual mat = new CryptoMaterialDual(signingCert, responseCert, sjc); // 1) Build your request JSON String requestJson = new org.json.JSONObject() .put("amount", "10.00") .put("currency", "USD") .put("reference", "ORDER-12345") .toString(); // 2) Encrypt request body to JWE using SJC public cert String encryptedJwe = encryptToJwe(requestJson, mat.sjcCert); // 3) Build the HTTP body (this is what you’ll hash for the digest) String httpBody = new org.json.JSONObject() .put("encryptedRequest", encryptedJwe) .toString(); // 4) Build JWS payload: include iat, response kid, digestAlgorithm, and digest of httpBody String digestB64 = sha256Base64(httpBody); String jwsPayload = new org.json.JSONObject() .put("iat", java.time.Instant.now().getEpochSecond()) .put("v-c-api-response-mle-kid", kidFromCert(mat.responseCert.cert)) // instruct server to encrypt to your API Response MLE key .put("digestAlgorithm", "SHA-256") .put("digest", digestB64) .toString(); // 5) Sign the JWS with the REST – Certificate private key String signedJws = signAsJws(jwsPayload, mat.signingCert); // 6) Send the HTTP request // POST /your/api // Content-Type: application/json // Authorization: Bearer <signedJws> /* Body: { "encryptedRequest": "<encryptedJwe>" } */ // 7) Handle the response (decrypt if needed with API Response MLE private key) String apiResponse = /* http call result as string */; org.json.JSONObject resp = new org.json.JSONObject(apiResponse); String finalPayload = resp.has("encryptedResponse") ? decryptJwe(resp.getString("encryptedResponse"), mat.responseCert) : apiResponse;