![[CyberSource logo]](images/cybslogo.gif)
Search documentation:
|
|
Search documentation: |
| Help Advanced | |
| Published 05/13/2002 |
|
Chapter 2
Incorporating Smart Authorization into Your Order Flow
This chapter offers options for addressing customer service issues by using information provided by risk factor codes and by taking measures to convert support calls into sales. This chapter includes the following sections:
Interpreting the Result
Smart Authorization uses risk factor codes, which provide additional information about the level of risk, to help you assist customers whose orders have been declined. These codes provide valuable information for your customer service representatives, helping them decide how best to resolve customer inquiries.
Risk factor codes enable customer service representatives to identify reasons for a high risk level and to complete sales that look suspicious but that are actually good orders.
Risk factor codes are returned to you in the auth_factor_code field. CyberSource replies with all applicable factor codes, not just the most severe. Table 2 contains the list of factors with a brief description of each.
As a merchant, you are encouraged to build custom support screens that integrate the risk factor codes into your customer service process. These fields are also displayed on the support screens that CyberSource provides. In some cases, you might prefer to use these results to decipher and filter the risk factor codes, in real time, to initiate proactive customer service measures.
Table 2 Risk Factor CodesEffective Customer Communication
When a transaction has been declined, present a message that encourages the customer to contact your customer service representatives. Do not imply that your customer has committed fraud.
Example Do's and Don'ts in Customer Communication
- Do display a message similar to this when a transaction is declined.
- "
We are having difficulty processing your transaction. Please contact us at 1-800-nnn-nnnn."- Do display a message similar to the following in the case of system error:
- "
We are having difficulty processing the order. Please contact us at 1-800-nnn-nnnnto place your order by phone, or please try again later."- Do not display a message similar to the following:
- "
This appears to be a fraudulent order."- Do not display a message similar to the following:
- "
CyberSource says you are a fraudulent customer."Your first level of customer service is the message you return when you uncover a problem with the order. Many of the calls you receive are likely to be from legitimate customers who receive a high risk result due to typographical errors or unique order profiles.
Maximizing Sales and Profits
To provide optimal customer service, contact customers with questionable orders even if their orders are not declined. This contact decreases the incidence of risk and increases customer service for those customers who need help. To do this, define three categories of orders: good, suspicious (pending follow-up), and known bad. Consider doing the following:
- Flag orders that were initially declined, but later converted into a legitimate sale. Identify patterns in these orders to decrease your insult rate.
- Refer suspicious transactions to your call center.
Sample Order Flow
The following section explains how to create an order flow that includes Smart Authorization.
Sequence of Events for a Transaction
Four outcomes are possible when you submit a request order for Smart Authorization:
- The order passes authorization and risk screening. You approve the transaction.
- The order passes authorization and fails risk screening, but is accepted after you determine the order is a false positive. You approve the transaction.
- The order passes authorization and fails risk screening. You determine that the order is fraudulent and decline the transaction.
- The order fails authorization and passes risk screening. You determine that the order is fraudulent and decline the transaction.
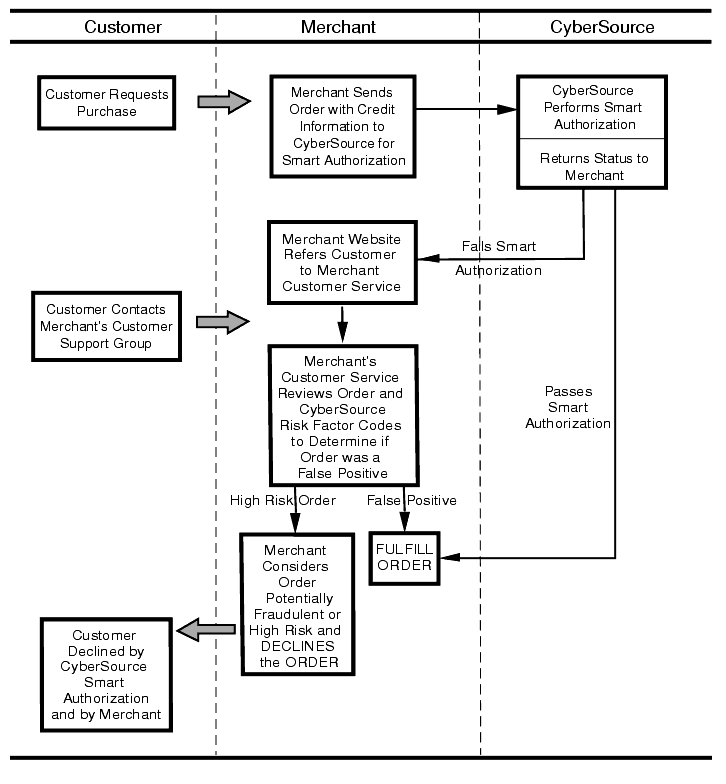
The following figure illustrates the flow of information between the customer, you and CyberSource for a declined or accepted transaction.
Figure 1 Order Flow Between Customer, Merchant and CyberSource
Conclusion
You are now equipped with the information you need to plan and implement Smart Authorization in your eCommerce site.
| Copyright © 2002 CyberSource Corporation. |